A heat pump is a refrigeration cycle device that converts low-potential thermal energy in the environment (air, water, or ground) into high-potential heat. This is a reversible device that can both heat and cool the building and provide hot water supply.

Four types of heat pumps are mainly used:
air/type of air - receives thermal energy from the surrounding ambient air and transfers it to the air in the building. This type of heat pump does not work at low ambient temperatures and does not produce hot water. It is considered as an addition to other heating systems. The reverse heat pump can also work in cooling mode - it cools the indoor air of the building by removing the warm air to the environment.
Air/water type - Takes energy from the ambient air and transfers it to the water heating system. Some models of modern heat pumps work even when the ambient temperature is minus 20°C, however, it is recommended to have an alternative heating element with the heat pump during negative ambient temperatures, which will act as a kind of helper and allow the heat pump to work in a comfortable working temperature range. allow. This type of heat pump can also be used for hot water supply.

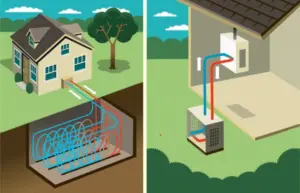
geothermal type (Geothermal water, other water/water type - receives energy from the earth's core, aquifer or river. It is possible to artificially arrange a pipe collector deep in the ground, which will take heating energy from the soil. This type of system is arranged, for example, on private houses that have their own yard and it is possible under the greenery of the yard Arrangement of the above-mentioned collectors.
Ground/water type - Takes heat from groundwater and transfers it to water. The working principle is very similar to the geothermal type.
Type of used air (exhausted air). (This type is the same as air/air) – reuses the energy (heat) that flows from the apartment through the ventilation channels and returns it to the heating system.
duration of work
The service life of air/water and water/water type heat pumps is about 20-30 years. In case of qualified installation, it will work smoothly throughout the year and will make your home comfortable.

heat pump The area of use is quite large, for example, they are used on such objects as: residential houses; hotels; restaurants; office-trade centers; schools and kindergartens; swimming pools; Enterprises and others. However, heat pumps are most widely used in small-scale facilities, such as private homes and swimming pools. We cannot call the heat pump the most budget system, therefore its use on large volume objects is not competitive from a financial point of view, although technological progress and refinement in the future will financially equalize the heat pump with other alternative systems.
History:
The heat pump was first designed and installed in 1855. Austrian engineer Peter Ritter von Rittinger is considered to be its inventor. The concept of the device was developed 3 years earlier by the British physicist and engineer William Thomson (Lord Kelvin).
A real demand for heat pumps arose and practical use began in the 1970s, when the topic of energy efficiency became relevant.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of:
Economy, as well as the ability to switch from winter heating mode to summer air conditioning mode.
Automatic management – ensures reliability of heat pump operation. During operation, the system does not require special services.
Compactness - (a sufficiently powerful heat pump module is no bigger than a regular refrigerator) and is practically silent during operation.
At least, we can name the relatively low temperature (not more than 50-60 degrees) during water heating. In addition, the higher the temperature of the heated water, the lower the efficiency of the heat pump (due to the increased - high pressure of the refrigerant in the system).
გაეცანით ჩვენს ბლოგს გათბობის სისტემებზე ამ ბმულზე.

